浅拷贝深拷贝
浅拷贝深拷贝
浅克隆
- 被复制对象的所有变量都含有与原来的对象相同的值,而所有的对其他对象的引用仍然指向原来的对象。即对象的浅拷贝会对“主”对象进行拷贝,但不会复制主对象里面的对象。”里面的对象“会在原来的对象和它的副本之间共享。浅拷贝仅仅复制所考虑的对象,而不复制它所引用的对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
class Score {
private int Math;
private int English;
private StringBuffer stringBuffer;
// get、set、构造器、toString
}
class Student implements Cloneable {
private String name;
private StringBuilder stringBuilder;
private int age;
private Integer integer;
private List<String> list;
private Score score;
private int[] arry;
// get、set、构造器、toString
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("xixi");
list.add("haha");
list.add("enen");
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("嘻嘻");
list2.add("哈哈");
list2.add("嗯嗯");
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("jjj");
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
stringBuffer.append("enenen");
int[] array = {1,2,3};
Score score = new Score(11, 11, stringBuffer);
Student student1 = new Student("哈哈", stringBuilder, 21, 10, list, score, array);
Student student2 = (Student) student1.clone();
Student student3 = student1; // 和student1是同一个对象
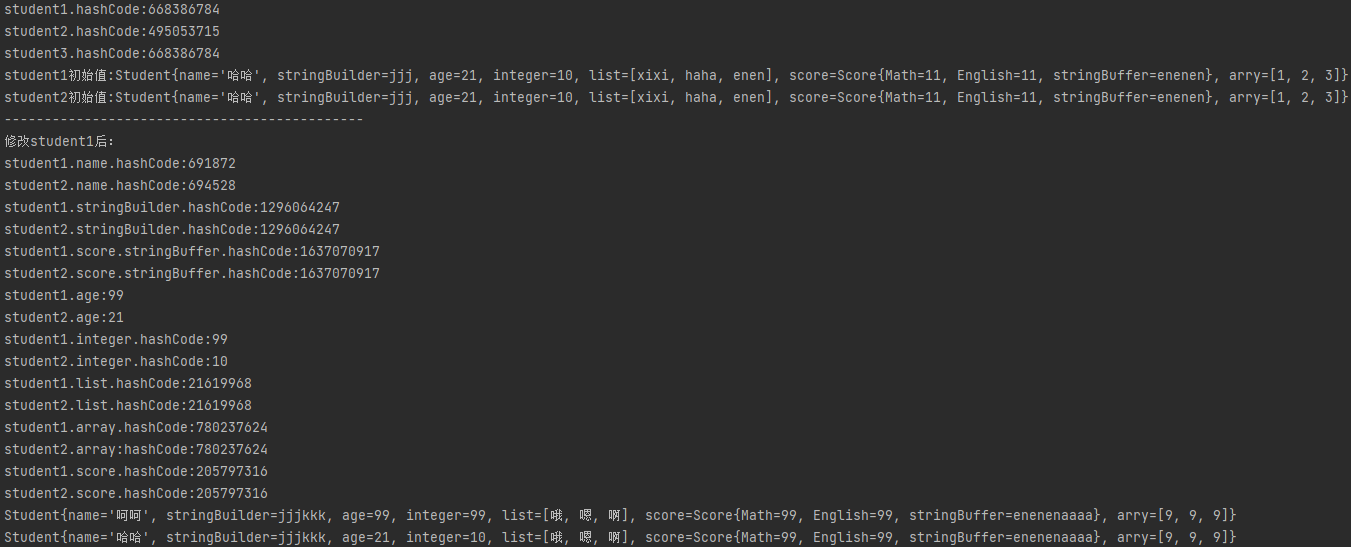
System.out.println("student1.hashCode:" + student1.hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.hashCode:" + student2.hashCode());
System.out.println("student3.hashCode:" + student3.hashCode());
System.out.println("student1初始值:" + student1);
System.out.println("student2初始值:" + student2);
System.out.println("---------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("修改student1后:");
// String被final修饰,属于不变的引用类型,深拷贝,改变他的值就会new出新对象
student1.setName("呵呵");
System.out.println("student1.name.hashCode:" + student1.getName().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.name.hashCode:" + student2.getName().hashCode());
// StringBuilder是可变引用类型,浅拷贝
stringBuilder.append("kkk");
System.out.println("student1.stringBuilder.hashCode:" + student1.getStringBuilder().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.stringBuilder.hashCode:" + student2.getStringBuilder().hashCode());
student1.getScore().getStringBuffer().append("aaaa");
System.out.println("student1.score.stringBuffer.hashCode:" + student1.getScore().getStringBuffer().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.score.stringBuffer.hashCode:" + student2.getScore().getStringBuffer().hashCode());
// 8种基本数据类型都是深拷贝
student1.setAge(99);
System.out.println("student1.age:" + student1.getAge());
System.out.println("student2.age:" + student2.getAge());
/**
* // integer的值是不可变的
* private final int value;
*
* // integer.hashCode()返回的就是integer的值
* @Override public int hashCode() {
* return Integer.hashCode(value);
* }
* public static int hashCode(int value) {
* return value;
* }
*
* 所有的包装类型都是不变的引用类型,包装类型直接就是深克隆
*/
// student1.setInteger(new Integer(99));
student1.setInteger(99); // 和new Integer(99)效果一样,都是一个新的Integer
System.out.println("student1.integer.hashCode:" + student1.getInteger().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.integer.hashCode:" + student2.getInteger().hashCode());
// student1.setList(list2); // 直接把student1的list对象换成一个新new出来的对象,hashCode不一样,
student1.getList().set(0, "哦"); // 对原来的list对象修改,student2和student1共用一个list对象,student2的list也会改
student1.getList().set(1, "嗯");
student1.getList().set(2, "啊");
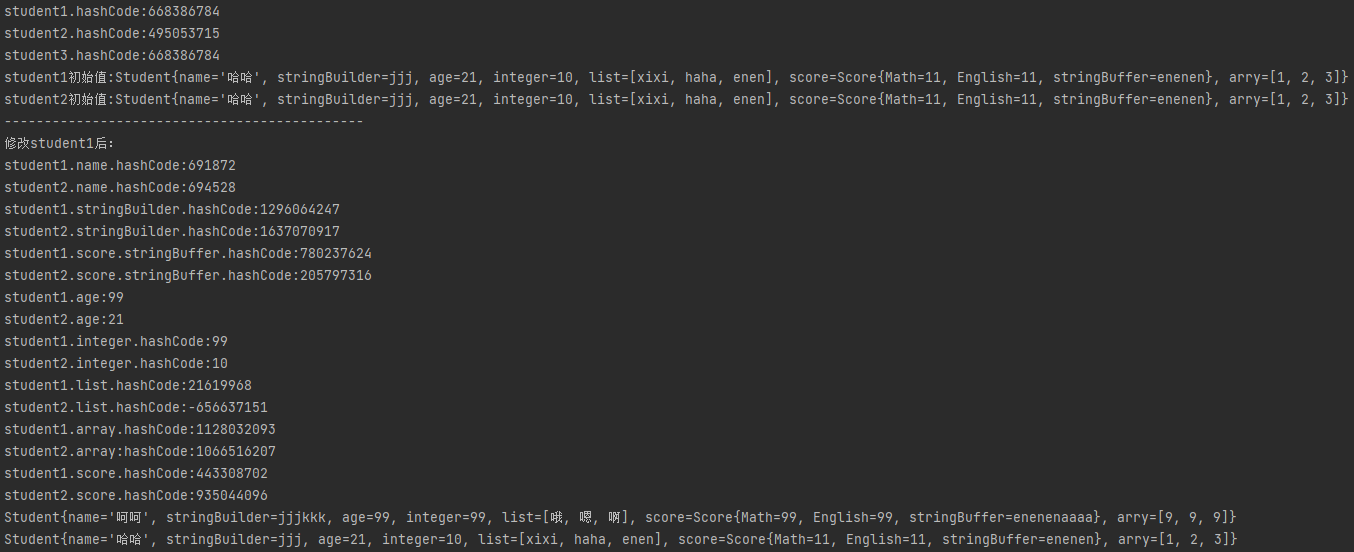
System.out.println("student1.list.hashCode:" + student1.getList().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.list.hashCode:" + student2.getList().hashCode());
// 数组也是可变引用对象
student1.getArry()[0] = 9;
student1.getArry()[1] = 9;
student1.getArry()[2] = 9;
System.out.println("student1.array.hashCode:" + student1.getArry().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.array:hashCode:" + student2.getArry().hashCode());
// student1.setScore(new Score(99,99));
student1.getScore().setMath(99);
student1.getScore().setEnglish(99);
System.out.println("student1.score.hashCode:" + student1.getScore().hashCode());
System.out.println("student2.score.hashCode:" + student2.getScore().hashCode());
System.out.println(student1);
System.out.println(student2);
}
}
- 运行结果
- ==8种基本类型和不可变的引用类型(被final修饰的包括String,8种包装类型)都是深拷贝。改变值都是新new出一个对象。==
深克隆
- 使Score实现Cloneable接口,重写clone()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Score score = (Score) super.clone();
// 只需要对stringBuffer处理,int本来就是深拷贝,不用处理
score.stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
score.stringBuffer.append(this.stringBuffer.toString());
return score;
}
- 修改Student.clone()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Student student = (Student) super.clone();
// 深拷贝stringBuilder
student.stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
student.stringBuilder.append(this.stringBuilder.toString());
// 深拷贝list
student.list = new ArrayList<>();
student.list.addAll(list);
// 深拷贝score
student.score = (Score) this.score.clone();
// 深拷贝array
student.arry = new int[this.arry.length];
for (int i = 0; i < this.arry.length; i++) {
student.arry[i] = this.arry[i];
}
return student;
}
- 运行结果
- ==可变引用类型都是浅拷贝。要深拷贝这个类需要在clone()方法里对类的所有可变引用型的对员,都重新new出一个对象,把原来的值赋给新的对象,返回新对象。==
1
2
3
// Cloneable 接口是一个标记接口,用来表示某个功能在执行的时候是合法的
public interface Cloneable {
}
没有引用类型字段时
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
class Writer implements Cloneable {
private int age;
private String name;
// get,set和构造函数
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Writer{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
- 如果一个类没有实现 Cloneable 接口,即便它重写了
clone()方法,依然是无法调用该方法进行对象克隆的,程序在执行clone()方法的时候会抛出 CloneNotSupportedException 异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Writer writer1 = new Writer(18, "二狗");
Writer writer2 = (Writer) writer1.clone();
System.out.println("浅拷贝后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
writer2.setName("铁蛋");
System.out.println("调整了 writer2 的 name 后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
/*
浅拷贝后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗'}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗'}
调整了 writer2 的 name 后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗'}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='铁蛋'}
*/
}
- 字符串 String 是不可变对象,一个新的值必须在字符串常量池中开辟一段新的内存空间,所以并没有影响到字符串二狗的值
有引用类型字段时
浅拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
class Book {
private String bookName;
private int price;
// get,set和构造函数
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString().substring(26) +
" bookName='" + bookName + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
class Writer implements Cloneable {
private int age;
private String name;
// 新加了个自定义的引用类型字段
private Book book;
// get,set和构造函数
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Writer{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", book=" + book +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Writer writer1 = new Writer(18,"二狗",new Book("编译原理",100));
Writer writer2 = (Writer) writer1.clone();
System.out.println("浅拷贝后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
Book book = writer2.getBook();
book.setBookName("离散数学");
book.setPrice(70);
System.out.println("writer2.book 变更后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
/*
浅拷贝后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='编译原理', price=100}}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='编译原理', price=100}}
writer2.book 变更后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='离散数学', price=70}}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='离散数学', price=70}}
*/
}
writer2.book 变更后,writer1.book 也发生了改变。自定义对象的内存地址并没有发生改变,只是对应的字段值发生了改变
==浅拷贝克隆的对象中,引用类型的字段指向的是同一个,当改变任何一个对象,另外一个对象也会随之改变,除去字符串的特殊性外==
深拷贝
- 深拷贝和浅拷贝不同的,深拷贝中的引用类型字段也会克隆一份,当改变任何一个对象,另外一个对象不会随之改变
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Book implements Cloneable{
private String bookName;
private int price;
// get,set和构造函数
@Override
public String toString() {
return super.toString().substring(26) +
" bookName='" + bookName + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
// 重写了 clone() 方法,并实现了 Cloneable 接口。为的就是深拷贝的时候也能够克隆该字段。
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return super.clone();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class Writer implements Cloneable {
private int age;
private String name;
private Book book;
// get,set和构造函数
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Writer{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", book=" + book +
'}';
}
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
// 不再只调用 Object 的 clone() 方法对 Writer 进行克隆了
Writer writer = (Writer) super.clone();
// 还对 Book 也进行了克隆
writer.setBook((Book) writer.getBook().clone());
return writer;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Writer writer1 = new Writer(18,"二狗",new Book("编译原理",100));
Writer writer2 = (Writer) writer1.clone();
System.out.println("深拷贝后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
Book book = writer2.getBook();
book.setBookName("离散数学");
book.setPrice(70);
System.out.println("writer2.book 变更后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
/*
深拷贝后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='编译原理', price=100}}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='编译原理', price=100}}
writer2.book 变更后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='离散数学', price=100}}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='离散数学', price=70}}
*/
}
- 通过
clone()方法实现的深拷贝比较笨重,因为要将所有的引用类型都重写clone()方法
使用序列化实现深拷贝
1
2
3
4
5
class Book implements Serializable {
private String bookName;
private int price;
...
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
class Writer implements Serializable {
private int age;
private String name;
private Book book;
...
//深度拷贝
public Object deepClone() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(this);
// 反序列化
ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);
return ois.readObject();
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Writer writer1 = new Writer(18, "二狗", new Book("编译原理", 100));
Writer writer2 = (Writer) writer1.deepClone();
System.out.println("深拷贝后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
Book book = writer2.getBook();
book.setBookName("离散数学");
book.setPrice(70);
System.out.println("writer2.book 变更后:");
System.out.println("writer1:" + writer1);
System.out.println("writer2:" + writer2);
/*
深拷贝后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='编译原理', price=100}}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='编译原理', price=100}}
writer2.book 变更后:
writer1:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='离散数学', price=100}}
writer2:Writer{age=18, name='二狗', book=86 bookName='离散数学', price=70}}
*/
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权