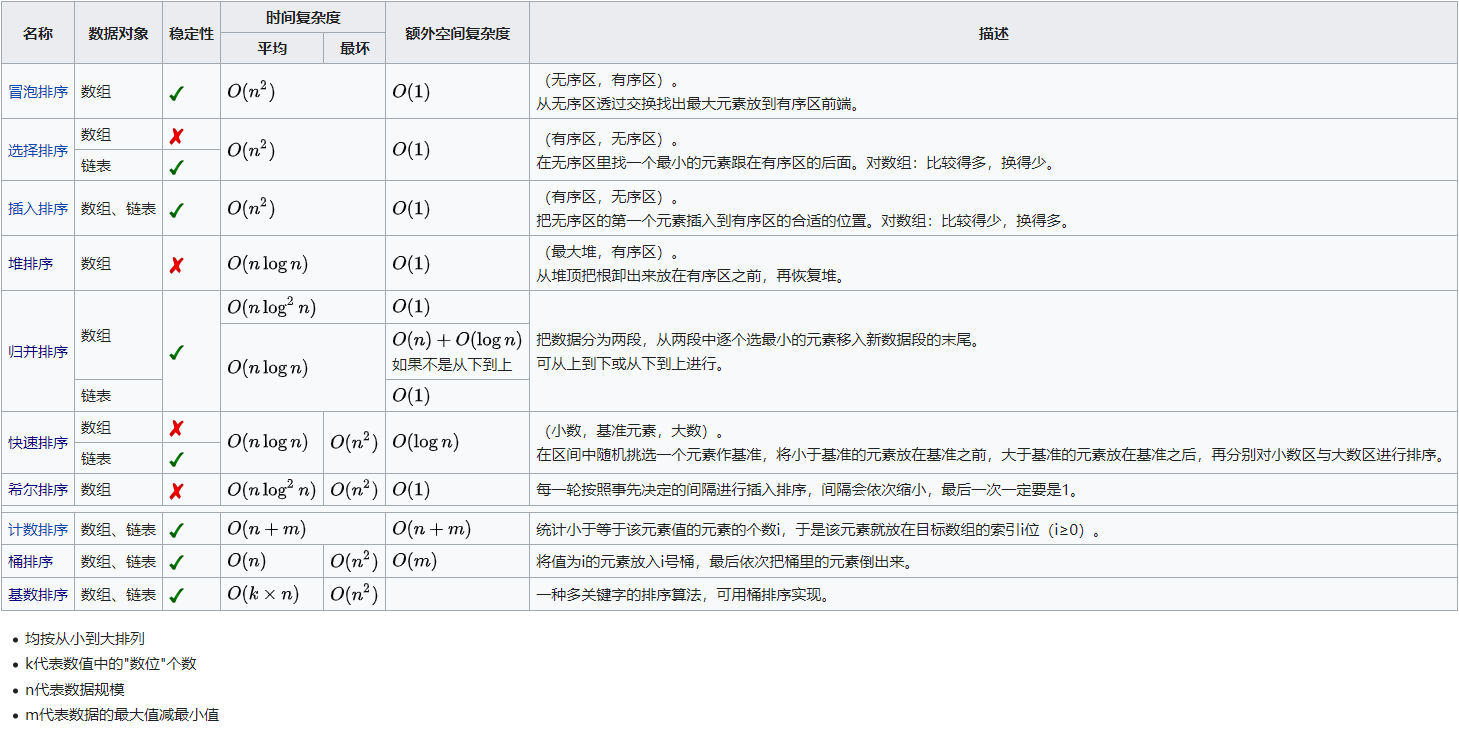
排序
排序是将数据按特定顺序排列的过程,常见算法有冒泡排序、选择排序、插入排序、快速排序和归并排序。
排序
排序
比较
分类
比较排序的时间复杂度的下界O(nlogn)
对于n个待排序元素,在未比较时,可能的正确结果有n!种。在经过一次比较后,其中两个元素的顺序被确定,所以可能的正确结果剩余n!/2种(确定之前两个元素的前后位置的情况是相同,确定之后相当于少了一半的可能性)。依次类推,直到经过m次比较,剩余可能性n!/(2\^m)种。直到n!/(2^m)<=1时,结果只剩余一种。根据斯特灵公式,此时的比较次数m为o(nlogn)次。所以基于排序的比较算法,最优情况下,复杂度是O(nlogn)的。
源码
C版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
/**
* @file Sort.cpp
* @author Sprinining (Sprinining@gmail.com)
* @brief 交换排序:冒泡排序、快速排序
* 选择排序:普通选择排序、堆排序
* 插入排序:直接插入排序、二分插入排序、希尔排序
* 归并排序:普通归并排序
* 分布排序:计数排序、桶排序、基数排序
* @version 0.1
* @date 2022-05-06
*
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2022
*
*/
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int cmp(const void* a, const void* b) { return *(int*)(a) - *(int*)b; }
void swap(int* a, int* b) {
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// a, b不能是同一个地址的东西,否则会把该地址清零
void swap2(int* a, int* b) {
*a = *a ^ *b;
*b = *a ^ *b;
*a = *a ^ *b;
}
void display(int* ary, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
printf("%d ", ary[i]);
}
puts("");
}
// 1.冒泡排序
void bubbleSort(int* array, int size) {
// 比较size-1轮
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
// 是否已经有序了
bool isSorted = true;
// 每一轮都会有个大元素移到后面
for (int j = 0; j < size - 1 - i; j++) {
// 将相邻的两个比较,大的移到后面
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
// 有交换的说明没排好
isSorted = false;
swap(&array[j], &array[j + 1]);
}
}
if (isSorted == true) break;
}
display(array, size);
}
void quickSortRecursive(int* array, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return;
int i = left;
int j = right;
// 基准元素
int key = array[left];
// 分成两半,左边小于基准元素,右边大于基准元素
while (i < j) {
// 从右往左找第一个小于key的
while (i < j && array[j] >= key) {
j--;
}
// 与key交换
if (i < j) {
array[i] = array[j];
// array[j]不用立刻放入key,后面可能会有比key大的元素防止这
i++;
}
// 从左往右找第一个大于key的
while (i < j && array[i] <= key) {
i++;
}
// 与key交换
if (i < j) {
array[j] = array[i];
j--;
}
}
// 循环退出时i=j
array[i] = key;
quickSortRecursive(array, left, i - 1);
quickSortRecursive(array, i + 1, right);
}
// 2.快速排序
void quickSort(int* array, int size) {
quickSortRecursive(array, 0, size - 1);
display(array, size);
}
// 3.普通选择排序
void selectionSort(int* array, int size) {
// size-1轮
for (int i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
// 从后面找更小的
for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++) {
if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
// 确实有更小的
if (minIndex != i) {
swap(&array[i], &array[minIndex]);
}
}
display(array, size);
}
// 自顶向下调整堆顶(只有堆顶不符合堆的定义)
void adjustHeap(int* array, int currentIndex, int size) {
int temp = array[currentIndex];
int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
while (leftChildIndex <= (size - 1)) {
// 找更大点的子节点
if (leftChildIndex < (size - 1) &&
array[leftChildIndex] < array[leftChildIndex + 1]) {
leftChildIndex++;
}
// 更大的子节点都比 temp 小,那就不需要再往下调整了
if (array[leftChildIndex] <= temp) break;
// 与子节点交换
array[currentIndex] = array[leftChildIndex];
// 调整子节点往下的分支
currentIndex = leftChildIndex;
leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
}
array[currentIndex] = temp;
}
// 4.堆排序(下标从0开始)
void heapSort(int* array, int size) {
// 从第一个非叶子节点开始,自底向上
for (int i = (size - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(array, i, size);
}
printf("大顶堆:");
display(array, size);
// size-1轮
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
swap(&array[0], &array[size - i]);
// 已经是堆了,在修改完堆顶后只需要对堆顶进行重定位
adjustHeap(array, 0, size - i);
}
display(array, size);
}
// 5.直接插入排序
void insertionSort(int* array, int size) {
// size-1轮
// [0, i-1]是有序序列
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
// 待插入的元素
int temp = array[i];
// 插入已经有序的序列
// 从有序序列的末尾往前找第一个小于等于temp的
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && (array[j] > temp)) {
// 边找边把不符合的元素后移
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j--;
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
display(array, size);
}
// 6.二分插入排序
void binaryInsertionSort(int* array, int size) {
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
// 二分查找插入位置
int left = 0;
int right = i - 1;
int mid;
while (left <= right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (array[mid] >= temp) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 循环结束后left就是应该插入的下标
// 把下标从left到i-1的都往后移动一位
for (int j = i - 1; j >= left; j--) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
}
array[left] = temp;
}
display(array, size);
}
// 7.希尔排序
void shellSort(int* array, int size) {
// 步长(让一个元素可以一次性地朝最终位置前进一大步)
int gap = size / 2;
while (gap > 0) {
// 间隔gap的分在同一组(共gap组,gap下标[0,
// gap-1]是这gap组每组的首个已排序元素),进行普通的插入排序
for (int i = gap; i < size; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j = i - gap;
while (j >= 0 && array[j] > temp) {
array[j + gap] = array[j];
j -= gap;
}
array[j + gap] = temp;
}
printf("gap:%d\n", gap);
display(array, size);
gap = gap / 2;
}
}
// 分治-治
void mergeSort_conquer(int* array, int left, int mid, int right, int* temp) {
// [left, mid]和[mid+1, right]两个有序数组
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int index = 0;
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
if (array[i] < array[j]) {
temp[index++] = array[i++];
} else {
temp[index++] = array[j++];
}
}
// 剩余元素直接放入temp
while (i <= mid) {
temp[index++] = array[i++];
}
while (j <= right) {
temp[index++] = array[j++];
}
// 放回原数组
index = 0;
while (left <= right) {
array[left++] = temp[index++];
}
}
// 分治-分
void mergeSort_divide(int* array, int left, int right, int* temp) {
if (left >= right) return;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 左边归并排序
mergeSort_divide(array, left, mid, temp);
// 右边归并排序
mergeSort_divide(array, mid + 1, right, temp);
// 合并两个有序序列
mergeSort_conquer(array, left, mid, right, temp);
}
// 8.普通归并排序
void mergeSort(int* array, int size) {
int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
mergeSort_divide(array, 0, size - 1, temp);
display(array, size);
}
// TODO: 迭代版归并排序
// 9.计数排序(每个桶只存储单一键值) 0~10
void countingSort(int* array, int size) {
int* frequency = (int*)calloc(11, sizeof(int));
// frequency[i]表示统计i出现的次数
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
frequency[array[i]]++;
}
display(frequency, 11);
// frequency[i]表示小于等于i的个数
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
frequency[i] += frequency[i - 1];
}
display(frequency, 11);
int* sorted = (int*)calloc(size, sizeof(int));
// 倒着遍历原数组,把原数组放在新数组正确的位置上
for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 有frequency[array[i]]个小于等于array[i]个元素
// 说明array[i]排在第frequency[array[i]]个位置,下标就是frequency[array[i]]-1
// 放好后frequency[array[i]]要自减
sorted[--frequency[array[i]]] = array[i];
printf("frequency:\t");
display(frequency, 11);
printf("sorted:\t\t");
display(sorted, size);
}
}
typedef struct {
int** bucket;
int row;
int column;
int* index;
} Bucket;
// 10.桶排序(每个桶存储一定范围的数值)
// 数要相对均匀分布,桶的个数也要合理设计(需要知道输入数据的上界和下界和分布情况),桶排序是一种用空间换取时间的排序
void bucketSort(int* array, int size) {
Bucket* b = (Bucket*)malloc(sizeof(Bucket));
b->row = 5;
b->column = 3;
b->index = (int*)calloc(b->row, sizeof(int));
b->bucket = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int) * b->row);
for (int i = 0; i < b->row; i++) {
b->bucket[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * b->column);
}
// 放入桶
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int index = array[i] / 10;
b->bucket[index][b->index[index]++] = array[i];
}
size = 0;
// 对每个桶进行排序(可用其他算法)
for (int i = 0; i < b->row; i++) {
qsort(b->bucket[i], b->column, sizeof(int), cmp);
for (int j = 0; j < b->column; j++) {
array[size++] = b->bucket[i][j];
}
}
display(array, size);
}
// 11.基数排序(根据键值的每位数字来分配桶)
void radixSort(int* array, int size) {
Bucket* b = (Bucket*)malloc(sizeof(Bucket));
b->row = 10;
b->column = 10;
b->index = (int*)calloc(b->row, sizeof(int));
// 临时存放按某一位排好序的序列
b->bucket = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int) * b->row);
for (int i = 0; i < b->row; i++) {
b->bucket[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * b->column);
}
// 最大的数的位数为3
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// 按某一位重新排序
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) {
int index = (array[j] / (int)pow(10, i)) % 10;
b->bucket[index][b->index[index]++] = array[j];
}
// 放回原数组
int returnSize = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < b->row; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < b->index[j]; k++) {
array[returnSize++] = b->bucket[j][k];
}
// 重置下标数组
b->index[j] = 0;
}
}
display(array, size);
}
void testSort() {
// int a[] = {1, 0, 7, 2, 10, 5, 2, 8, 6, 0};
// display(a, 10);
// bubbleSort(a, 10);
// quickSort(a, 10);
// selectionSort(a, 10);
// heapSort(a, 10);
// insertionSort(a, 10);
// binaryInsertionSort(a, 10);
// shellSort(a, 10);
// mergeSort(a, 10);
// countingSort(a, 10);
// int b[] = {1, 8, 7, 44, 42, 46, 38, 34, 33, 17, 15, 16, 27, 28, 24};
// display(b, 15);
// bucketSort(b, 15);
int c[] = {53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 77, 214, 154, 63, 616};
radixSort(c, 10);
}
- 双轴快排
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
void daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(int* array, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return;
int i = left;
int j = right;
int k = i + 1;
// 小于等于pivot1:区间A=[left, i]
// 大于等于pivot2:区间B=[j, right]
// 两者之间:区间C=[i+1, k-1]
// 待处理:区间D=[k, j-1]
// 对两个轴处理
if (array[left] > array[right]) {
swap(&array[left], &array[right]);
}
int pivot1 = array[left];
int pivot2 = array[right];
while (k < j) {
if (array[k] > pivot1 && array[k] < pivot2) {
k++;
} else if (array[k] <= pivot1) {
// 把C的首个元素与当前元素交换,首个元素还在C中
swap(&array[++i], &array[k++]);
} else if (array[k] >= pivot2) {
// 从右往左找第一个比pivot2小的元素
while (k < j && array[j] >= pivot2) {
j--;
}
// k不用自增,j也不用自减
swap(&array[k], &array[j]);
}
}
// 把轴移到该放的位置
swap(&array[left], &array[i]);
swap(&array[right], &array[j]);
// 对两个轴分出的三个区间进行递归调用
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, left, i - 1);
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, i + 1, j - 1);
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, j + 1, right);
}
// 12.双轴快排
void daulPivotQuickSort(int* array, int size) {
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, 0, size - 1);
display(array, size);
}
Java版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
package sort;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Sort {
// 对数器
public static boolean check(int count) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
if (!isArrayEqual())
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isArrayEqual() {
int size = (int) (Math.random() * 100);
int[] array = generateRandomArray(size);
int[] temp = Arrays.copyOf(array, array.length);
Arrays.sort(array);
// bubbleSort(temp);
// quickSort(temp);
// daulPivotQuickSort(temp);
// selectionSort(temp);
// heapSort(temp);
// insertionSort(temp);
// binaryInsertionSrot(temp);
// shellSort(temp);
// mergeSort(temp);
// countingSort(temp);
// bucketSort(temp);
radixSort(temp);
return Arrays.equals(array, temp);
}
// 数组元素范围: [0, 999]
public static int[] generateRandomArray(int size) {
int[] res = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
res[i] = (int) (Math.random() * 1000);
}
return res;
}
public static void swap(int[] array, int a, int b) {
int temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
boolean isSorted = true;
for (int j = 1; j < array.length - i; j++) {
if (array[j - 1] > array[j]) {
swap(array, j - 1, j);
isSorted = false;
}
}
if (isSorted)
break;
}
}
public static void quickSort(int[] array) {
quickSortRecursive(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
public static void quickSortRecursive(int[] array, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right)
return;
int i = left;
int j = right;
int pivot = array[left];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && array[j] >= pivot) {
j--;
}
if (i < j) {
array[i] = array[j];
i++;
}
while (i < j && array[i] <= pivot) {
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
array[j] = array[i];
j--;
}
}
array[i] = pivot;
quickSortRecursive(array, left, i - 1);
quickSortRecursive(array, i + 1, right);
}
// 双轴快排
public static void daulPivotQuickSort(int[] array) {
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
public static void daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(int[] array, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right)
return;
int i = left;
int j = right;
int k = left + 1;
// A:[left, i]
// B:[i+1, k-1]
// C:[k, j-1]
// D:[j, right]
if (array[left] > array[right]) {
swap(array, left, right);
}
int pivot1 = array[left];
int pivot2 = array[right];
while (k < j) {
int temp = array[k];
if (temp > pivot1 && temp < pivot2) {
k++;
} else if (temp <= pivot1) {
swap(array, ++i, k++);
} else if (temp >= pivot2) {
while (k < j && array[j] >= pivot2) {
j--;
}
if (k < j) {
swap(array, k, j);
}
}
}
swap(array, left, i);
swap(array, j, right);
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, left, i - 1);
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, i + 1, j - 1);
daulPivotQuickSortRecursive(array, j + 1, right);
}
public static void selectionSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
int minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
if (array[minIndex] > array[j]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex != i) {
swap(array, i, minIndex);
}
}
}
public static void heapSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = (array.length - 2) / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(array, i, array.length);
}
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
swap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
adjustHeap(array, 0, array.length - 1 - i);
}
}
public static void adjustHeap(int[] array, int currentIndex, int len) {
int temp = array[currentIndex];
int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
while (leftChildIndex <= (len - 1)) {
if (leftChildIndex < (len - 1) && array[leftChildIndex] < array[leftChildIndex + 1]) {
leftChildIndex++;
}
if (array[leftChildIndex] <= temp)
break;
array[currentIndex] = array[leftChildIndex];
currentIndex = leftChildIndex;
leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
}
array[currentIndex] = temp;
}
public static void insertionSort(int[] array) {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && array[j] > temp) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
j--;
}
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
public static void binaryInsertionSrot(int[] array) {
for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
int temp = array[i];
int left = 0;
int right = i - 1;
int mid;
while (left <= right) {
mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (array[mid] >= temp) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
for (int j = i - 1; j >= left; j--) {
array[j + 1] = array[j];
}
array[left] = temp;
}
}
public static void shellSort(int[] array) {
int gap = array.length / 2;
while (gap > 0) {
for (int i = gap; i < array.length; i += gap) {
int temp = array[i];
int j = i - gap;
while (j >= 0 && array[j] > temp) {
array[j + gap] = array[j];
j -= gap;
}
array[j + gap] = temp;
}
gap /= 2;
}
}
public static void mergeSort(int[] array) {
int[] temp = new int[array.length];
mergeSort_divide(array, 0, array.length - 1, temp);
}
public static void mergeSort_divide(int[] array, int left, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left >= right)
return;
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
mergeSort_divide(array, left, mid, temp);
mergeSort_divide(array, mid + 1, right, temp);
mergeSort_conquer(array, left, mid, right, temp);
}
public static void mergeSort_conquer(int[] array, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) {
if (left >= right)
return;
int i = left;
int j = mid + 1;
int index = 0;
while ((i <= mid && j <= right)) {
if (array[i] <= array[j]) {
temp[index++] = array[i++];
} else {
temp[index++] = array[j++];
}
}
while (i <= mid) {
temp[index++] = array[i++];
}
while (j <= right) {
temp[index++] = array[j++];
}
index = 0;
while (left <= right) {
array[left++] = temp[index++];
}
}
public static void countingSort(int[] array) {
int[] frequency = new int[1000];
for (int j : array) {
frequency[j]++;
}
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) {
frequency[i] += frequency[i - 1];
}
int[] sorted = new int[array.length];
for (int j : array) {
sorted[--frequency[j]] = j;
}
System.arraycopy(sorted, 0, array, 0, array.length);
}
public static void bucketSort(int[] array) {
// 数组元素范围: [0, 999]
// 十个桶: [0, 99], [100, 199] ...
List<List<Integer>> buckets = new ArrayList<>(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buckets.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int i : array) {
int index = i / 100;
buckets.get(index).add(i);
}
// 每个桶可以用其他的排序方法
int index = 0;
for (List<Integer> bucket : buckets) {
Collections.sort(bucket);
for (Integer integer : bucket) {
array[index++] = integer;
}
}
}
public static void radixSort(int[] array) {
// 数组元素范围: [0, 999]
// 十进制要十个桶,[0, 9]
List<List<Integer>> buckets = new ArrayList<>(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
buckets.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// 3位要三次循环
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j : array) {
int index = (j / (int) Math.pow(10, i)) % 10;
buckets.get(index).add(j);
}
// 写回
int index = 0;
for (List<Integer> bucket : buckets) {
for (Integer integer : bucket) {
array[index++] = integer;
}
bucket.clear();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 0, 7, 2, 10, 5, 2, 8, 6, 0};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
// bubbleSort(a);
// quickSort(a);
// daulPivotQuickSort(a);
// selectionSort(a);
// heapSort(a);
// insertionSort(a);
// binaryInsertionSrot(a);
// shellSort(a);
// mergeSort(a);
// countingSort(a);
// bucketSort(a);
radixSort(a);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
System.out.println(check(10000));
}
}
C++版
- 快排
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
void quickSort(vector<int> &array, int left, int right) {
if (left >= right) return;
int i = left;
int j = right;
int pivot = array[left];
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && pivot <= array[j]) {
j--;
}
if (i < j) {
array[i] = array[j];
i++;
}
while (i < j && pivot >= array[i]) {
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
array[j] = array[i];
j--;
}
}
array[i] = pivot;
quickSort(array, left, i - 1);
quickSort(array, i + 1, right);
}
- 堆排
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
// 自顶向下调整堆,len 是当前堆的大小,复杂度 O(logn)
void adjustHeap(vector<int> &array, int currentIndex, int len) {
// 要调整位置的元素
int temp = array[currentIndex];
// 左孩子下标
int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
// 自顶向下,调整到最后一个节点
while (leftChildIndex <= (len - 1)) {
// 把左右孩子中较大者的下标赋给 leftChildIndex
if (leftChildIndex < (len - 1)
&& (array[leftChildIndex] < array[leftChildIndex + 1]))
leftChildIndex++;
// 和当前元素比较大小,决定要不要调整堆
// 1. 不需要调整
if (array[leftChildIndex] <= temp) break;
// 2. 需要调整
array[currentIndex] = array[leftChildIndex];
currentIndex = leftChildIndex;
leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
}
// 放在最终的位置
array[currentIndex] = temp;
}
// [[堆........]] -> [[堆....][升序列表...]] -> [[升序列表......]]
void headSort(vector<int> &array) {
// 1. 建堆:从最后一个非叶子节点开始向上调整每个节点,复杂度 O(n)
// 最后一个非叶子节点下标为 n/2-1,下标从0开始
for (int i = array.size() / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(array, i, array.size());
}
// 2. n-1 轮排序:每次把大顶堆的堆顶移到末尾,并且堆的大小减一,最终形成升序列表
// 每次复杂度 O(logn),共 n-1 次,整体复杂度 O(nlogn)
for (int len = array.size() - 1; len >= 1; len--) {
// 把大顶堆的堆顶与末尾元素交换
swap(array[0], array[len]);
// 调整交换后的堆顶
adjustHeap(array, 0, len);
}
}
- C++ STL 版的堆排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int len;
vector<int> sortArray(vector<int>& nums) {
// 生成大根堆
make_heap(nums);
// 不断 pop,每次 pop 出的元素都放在堆的末尾的后一个位置
while (!is_heap_empty())
pop_heap(nums);
return nums;
}
bool is_heap_empty() {
return len == 0;
}
// 自顶向下调整堆
// 每次都是先向下,不断把孩子中的较大者往上移动,期间不和 value 比较
// 大概找到 value 的位置后,有可能需要再进行一次上浮操作
void adjust_heap(vector<int>& nums, int cur) {
// 起始位置
int top = cur;
int value = nums[cur];
int right_child = 2 * cur + 2;
while (right_child < len) {
// 选两个孩子的较大者
if (nums[right_child - 1] > nums[right_child])
right_child--;
// 无脑把较大者往上移动
nums[cur] = nums[right_child];
cur = right_child;
right_child = 2 * cur + 2;
}
if (right_child == len) {
nums[cur] = nums[right_child - 1];
cur = right_child - 1;
}
percolate_up(nums, top, cur, value);
}
// 生成大根堆
void make_heap(vector<int>& nums) {
len = nums.size();
// 最后一个非叶节点
for(int cur = (len - 2) / 2; cur >= 0; --cur)
adjust_heap(nums, cur);
}
// 交换堆顶堆尾,调整堆,堆大小减一
// 前提:nums 已经是大根堆
void pop_heap(vector<int>& nums) {
int value = nums[len - 1];
nums[len - 1] = nums[0];
nums[0] = value;
len--;
adjust_heap(nums, 0);
}
// cur 位置插入了 value,进行上浮调整
// top 是上浮到的顶部边界,主要是防止在 make_heap 调用的 adjust_heap 中上浮到不该上浮到的下标 0 位置
void percolate_up(vector<int>& nums, int top, int cur, int value) {
int parent = (cur - 1) / 2;
// 注意是 cur > top 而不是 parent >= top
while (cur > top && nums[parent] < value) {
nums[cur] = nums[parent];
cur = parent;
parent = (cur - 1) / 2;
}
nums[cur] = value;
}
}
- 基数排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
// 进制
static const int BASE = 10;
static const int MAXN = 50001;
static int help[MAXN];
static int cnts[BASE];
// 时间复杂度 O(n)
vector<int> sortArray(vector<int> &arr) {
if (arr.size() <= 1) return arr;
int n = arr.size();
int _min = arr[0];
// 找最小值
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
_min = min(_min, arr[i]);
int _max = 0;
// 先把整体减小,再找最大值
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] -= _min;
_max = max(_max, arr[i]);
}
// 根据最大值在 BASE 进制下的位数,决定基数排序做多少轮
radixSort(arr, n, bits(_max));
// 还原数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] += _min;
return arr;
}
// 返回 number 在 BASE 进制下有几位
int bits(int number) {
int ans = 0;
while (number > 0) {
ans++;
number /= BASE;
}
return ans;
}
// arr 内要保证没有负数,bits 是 arr 中最大值在 BASE 进制下有几位
void radixSort(vector<int> &arr, int n, int bits) {
for (int offset = 1; bits > 0; offset *= BASE, bits--) {
fill(cnts, cnts + BASE, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cnts[(arr[i] / offset) % BASE]++;
// 处理成前缀次数累加的形式
for (int i = 1; i < BASE; i++)
cnts[i] += cnts[i - 1];
// 直接定位到应该放到的位置
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--)
// 前缀数量分区的技巧
// 数字提取某一位的技巧
help[--cnts[(arr[i] / offset) % BASE]] = arr[i];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
arr[i] = help[i];
}
}
};
int Solution::help[MAXN] = {0};
int Solution::cnts[Solution::BASE] = {0};
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权