反射
反射
反射
简介
- 动态创建对象和编译,但对性能有影响(解释型操作)
- Class本身也是一个类
- Class对象只能由系统建立对象
- 一个加载的类在jvm中只会有一个Class实例
- 一个Class对象对应的是一个加载到jvm中的一个.class文件
- 每个类的实例都会记得自己是由哪个Class实例所生成
- 通过CLass可以完整的得到一个类中的所有被加载的结构
- Class类是Reflection的根源,想动态加载,必须先获得Class对象
缺点
- 破坏封装:由于反射允许访问私有字段和私有方法,所以可能会破坏封装而导致安全问题。
- 性能开销:由于反射涉及到动态解析,因此无法执行 Java 虚拟机优化
应用场景
- 开发通用框架:像 Spring,为了保持通用性,通过配置文件来加载不同的对象,调用不同的方法。
- 动态代理:在面向切面编程中,需要拦截特定的方法,就会选择动态代理的方式,而动态代理的底层技术就是反射。
- 注解:注解本身只是起到一个标记符的作用,它需要利用发射机制,根据标记符去执行特定的行为。
1
2
3
4
5
6
class CSer {
private String name;
private int mvp;
// get、set、构造器和toString
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
CSer niko = new CSer();
niko.setName("niko");
System.out.println(niko.getName());
// 获取反射类的 Class 对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("test.ReflectTest.CSer");
// 通过 Class 对象获取构造方法 Constructor 对象
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
// 通过 Constructor 对象初始化反射类对象
Object o = constructor.newInstance();
// 获取要调用的方法的 Method 对象
Method setNameMethod = clazz.getMethod("setName", String.class);
Method getNameMethod = clazz.getMethod("getName");
// 通过 invoke() 方法执行
setNameMethod.invoke(o, "glave");
System.out.println(getNameMethod.invoke(o));
}
invoke源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
boolean override;
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException,
InvocationTargetException {
// 如果方法不允许被覆盖,进行权限检查
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
// 检查调用者是否具有访问权限
checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers);
}
}
// 获取方法访问器(从 volatile 变量中读取)
MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile
if (ma == null) {
// 如果访问器为空,尝试获取方法访问器
ma = acquireMethodAccessor();
}
// 使用方法访问器调用方法,并返回结果
return ma.invoke(obj, args);
}
MethodAccessor接口有三个实现类,其中的MethodAccessorImpl是一个抽象类,另外两个具体的实现类继承了这个抽象类NativeMethodAccessorImpl:通过本地方法来实现反射调用;DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl:通过委派模式来实现反射调用;
1
2
3
4
// MethodAccessor接口
public interface MethodAccessor {
Object invoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
private MethodAccessor acquireMethodAccessor() {
// First check to see if one has been created yet, and take it
// if so
MethodAccessor tmp = null;
if (root != null) tmp = root.getMethodAccessor();
if (tmp != null) {
// 先判断是否存在对应的 MethodAccessor 对象,如果存在那么就复用之前的 MethodAccessor 对象
methodAccessor = tmp;
} else {
// Otherwise fabricate one and propagate it up to the root
// 否则调用 ReflectionFactory 对象的 newMethodAccessor 方法生成一个 MethodAccessor 对象
tmp = reflectionFactory.newMethodAccessor(this);
setMethodAccessor(tmp);
}
return tmp;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public MethodAccessor newMethodAccessor(Method var1) {
checkInitted();
if (noInflation && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(var1.getDeclaringClass())) {
return (new MethodAccessorGenerator()).generateMethod(var1.getDeclaringClass(), var1.getName(), var1.getParameterTypes(), var1.getReturnType(), var1.getExceptionTypes(), var1.getModifiers());
} else {
// 先是生成了一个 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 对象
NativeMethodAccessorImpl var2 = new NativeMethodAccessorImpl(var1);
// 再这个对象作为参数调用 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 类的构造方法
// 使用了代理模式,将 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 对象交给 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 对象代理
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl var3 = new DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(var2);
var2.setParent(var3);
return var3;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
class DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private MethodAccessorImpl delegate;
// 将 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 对象赋值给 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 类的 delegate 属性
DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl(MethodAccessorImpl var1) {
this.setDelegate(var1);
}
// ReflectionFactory 类的 newMethodAccessor 方法最终返回 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 类对象。所以我们在前面的 ma.invoke() 里,其将会进入 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 类的 invoke 方法中。
public Object invoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// 这里调用了 delegate 属性的 invoke 方法,它又有两个实现类,分别是:DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 和 NativeMethodAccessorImpl。按照我们前面说到的,这里的 delegate 其实是一个 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 对象,所以这里会进入 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 的 invoke 方法。
return this.delegate.invoke(var1, var2);
}
void setDelegate(MethodAccessorImpl var1) {
this.delegate = var1;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class NativeMethodAccessorImpl extends MethodAccessorImpl {
private final Method method;
private DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl parent;
private int numInvocations;
NativeMethodAccessorImpl(Method var1) {
this.method = var1;
}
public Object invoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) throws IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
// 如果超过该阀值,那么就会生成另一个MethodAccessor 对象,并将原来 DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl 对象中的 delegate 属性指向最新的 MethodAccessor 对象
if (++this.numInvocations > ReflectionFactory.inflationThreshold() && !ReflectUtil.isVMAnonymousClass(this.method.getDeclaringClass())) {
MethodAccessorImpl var3 = (MethodAccessorImpl)(new MethodAccessorGenerator()).generateMethod(this.method.getDeclaringClass(), this.method.getName(), this.method.getParameterTypes(), this.method.getReturnType(), this.method.getExceptionTypes(), this.method.getModifiers());
this.parent.setDelegate(var3);
}
return invoke0(this.method, var1, var2);
}
void setParent(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl var1) {
this.parent = var1;
}
private static native Object invoke0(Method var0, Object var1, Object[] var2);
}
- 第一次加载的时候使用的是 NativeMethodAccessorImpl 的实现,而当反射调用次数超过 15 次之后(可以通过
-Dsun.reflect.inflationThreshold参数类调整),则使用 MethodAccessorGenerator 生成的 MethodAccessorImpl 对象去实现反射。
获取反射类的Class对象
获取Class对象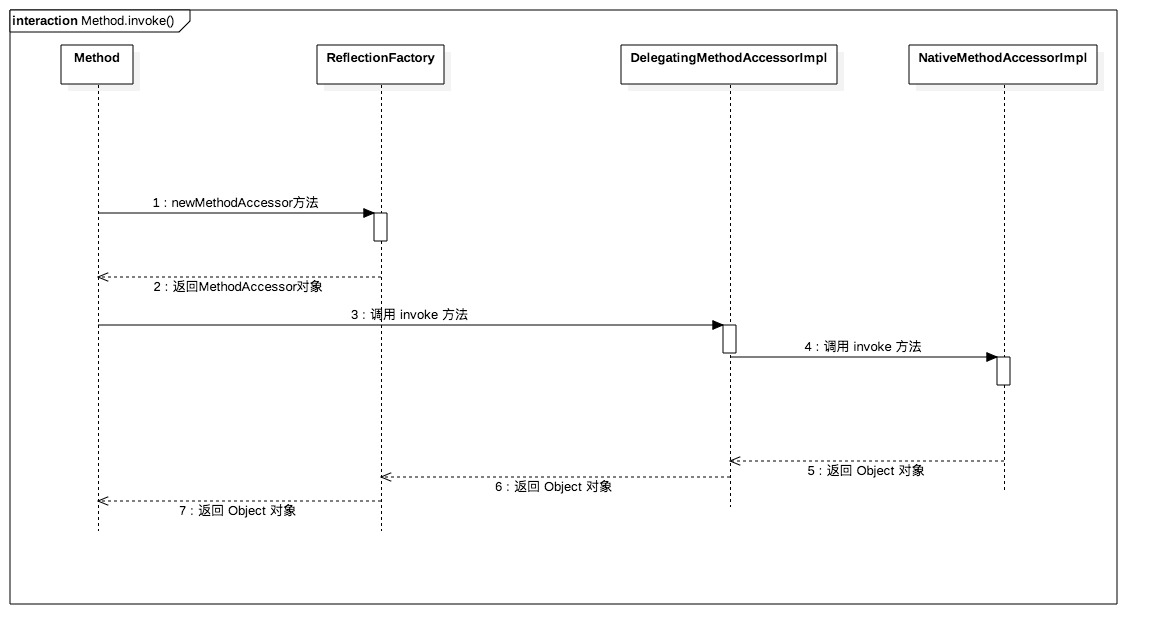
- Class.forName(),参数为反射类的完全限定名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Class c1 = Class.forName("test.ReflectTest.CSer");
// test.ReflectTest.CSer
System.out.println(c1.getCanonicalName());
Class c2 = Class.forName("[D");
// double[]
System.out.println(c2.getCanonicalName());
Class c3 = Class.forName("[[Ljava.lang.String;");
// java.lang.String[][]
System.out.println(c3.getCanonicalName());
- 类名.class,只适合在编译前就知道操作的 Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Class c1 = CSer.class;
// test.ReflectTest.CSer
System.out.println(c1.getCanonicalName());
Class c2 = String.class;
// java.lang.String
System.out.println(c2.getCanonicalName());
Class c3 = int[][][].class;
// int[][][]
System.out.println(c3.getCanonicalName());
- .getClass()
1
2
3
4
CSer cSer = new CSer();
Class clazz = cSer.getClass();
// test.ReflectTest.CSer
System.out.println(clazz.getCanonicalName());
所有类型的Class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Object> c1 = Object.class; // class java.lang.Object
Class<Comparable> c2 = Comparable.class; // interface java.lang.Comparable
Class<String[]> c3 = String[].class; // class [Ljava.lang.String;
Class<int[][]> c4 = int[][].class; // class [[I
Class<Override> c5 = Override.class; // interface java.lang.Override
Class<ElementType> c6 = ElementType.class; // class java.lang.annotation.ElementType
Class<Integer> c7 = Integer.class; // class java.lang.Integer
Class<Void> c8 = void.class; // void
Class<Class> c9 = Class.class; // class java.lang.Class
// 只要元素类型和维度一样,就是同一个Class
int[] a = new int[10];
int[] b = new int[1000];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode()); // 668386784
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode()); // 668386784
}
}
创建反射类的对象
- 用 Class 对象的
newInstance()方法
1
2
Class clazz = CSer.class;
CSer cSer = (CSer) clazz.newInstance();
- 用 Constructor 对象的
newInstance()方法
1
2
3
Class clazz = CSer.class;
Constructor constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
CSer cSer = (CSer) constructor.newInstance();
获取构造方法
getConstructor():返回反射类的特定 public 构造方法,可以传递参数,参数为构造方法参数对应 Class 对象;缺省的时候返回默认构造方法。getDeclaredConstructor():返回反射类的特定构造方法,不限定于 public 的。getConstructors():返回类的所有 public 构造方法。getDeclaredConstructors():返回类的所有构造方法,不限定于 public 的。
1
2
3
4
Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = String.class.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor<?> declaredConstructor : declaredConstructors) {
System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
}
获取字段和方法
- 同上,把关键字Constructor换成Field或Method
- 在访问私有方法和字段时,我们需要调用
setAccessible(true)方法来允许访问
获取运行时类的完整结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
package Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class<?> c1 = Class.forName("Reflection.User");
User user = new User();
c1 = user.getClass();
// 获得类的名字
System.out.println(c1.getName());// 包名 + 类名
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName());// 类名
// 获得类的属性
Field[] fields = c1.getDeclaredFields();// 找到全部属性 而getFields()只能找到public属性
for(Field field: fields){
System.out.println(field);
}
// 获得指定属性
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);
// 获得类的方法
Method[] methods = c1.getMethods();// 获得本类和父类的全部public方法
for(Method method:methods){
System.out.println(method);
}
methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods();// 获得本类全部方法,包括私有的
for(Method method:methods){
System.out.println(method);
}
// 获得指定方法
// 因为有重载所以要加参数
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
Method setName = c1.getMethod("setName", String.class);
System.out.println(getName);
System.out.println(setName);
// 获得全部的构造器
Constructor<?>[] constructors = c1.getConstructors();
for(Constructor constructor:constructors){
System.out.println(constructor);
}
constructors = c1.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor constructor:constructors){
System.out.println(constructor);
}
// 获得指定的构造器
Constructor<?> declaredConstructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class, int.class);
System.out.println(declaredConstructor);
}
}
动态创建对象执行方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
package Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("Reflection.User");
// 通过构造器创建对象
User user = (User)c1.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();// 调用的是无参构造器
System.out.println(user);
User user2 = (User)c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,int.class).newInstance("haha", 1, 2);
System.out.println(user2);
// 通过反射调用普通方法
User user3 = (User) c1.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
setName.invoke(user3, "xixi");// 激活 (对象,方法的值)
System.out.println(user3.getName());
// 通过反射操作属性
User user4 = (User) c1.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);// 不能直接操作私有属性,需要关闭安全检测
name.set(user4, "hehe");
System.out.println(user4.getName());
}
}
- 性能检测
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
package Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test9 {
// 普通方式调用
public static void test1(){
User user = new User();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10_0000_0000; i++) {
user.getName();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
// 反射方式调用
public static void test2() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10_0000_0000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user,null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
// 反射方式调用 关闭检测
public static void test3() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
Class c1 = user.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getMethod("getName", null);
getName.setAccessible(true);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 10_0000_0000; i++) {
getName.invoke(user,null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
test1();
test2();
test3();
/**
* 10ms
* 3651ms
* 1656ms
*/
}
}
类加载内存分析
- 类的加载过程
- 加载:将类的class文件读入内存,并为之创建一个==java.lang.Class对象==。此过程由类加载器完成
- 链接:将类的二进制数据合并到JRE中,正式为类变量(static)分配内存并设置类变量==默认初始值==
- 初始化:jvm负责对类进行初始化<clinit>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
package Reflection;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
System.out.println(A.m);
/**
* 1.加载到内存,产生一个类对应的Class对象
* 2.链接,链接结束后m=0
* 3.初始化
* <clinit>(){
* System.out.println("A类静态代码块");
* m = 300;
* m = 100;
* }
*/
}
}
class A{
static {
System.out.println("A类静态代码块");
m = 300;
}
static int m = 100;
public A(){
System.out.println("A类的无参构造");
}
}
- 何时发生类初始化
- 主动引用(发生初始化)
- jvm启动时,先初始化main所在的类
- new一个类的对象
- 调用类的静态成员(除了final常量)和静态方法
- 使用java.lang.reflect包的方法对类进行反射调用
- 初始化一个类,如果他的父类没有初始化,会先初始化父类
- 被动引用(不发生)
- 访问一个静态域时,只有真正声明这个域的类才会被初始化,如通过子类引用父类的静态变量,不会导致子类初始化
- 通过数组定义类引用,不会触发此类的初始化
- 引用常量不会触发(常量在链接阶段就存入调用类的常量池中了)
- 主动引用(发生初始化)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
package Reflection;
public class Test5 {
static {
System.out.println("Main类加载");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 主动引用
// Son son = new Son();
// 反射产生主动引用
// Class.forName("Reflection.Son");
/**
* Main类加载
* father加载
* son加载
*/
// 不会产生类的引用的方法
// System.out.println(Son.b);// 子类不会加载
// Son[] array = new Son[5];// 只有Main类加载了
System.out.println(Son.M);// 只有Main类加载了
}
}
class Father{
static int b = 2;
static {
System.out.println("father加载");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
static {
System.out.println("son加载");
m = 300;
}
static int m = 100;
static final int M = 1;
}
- 类加载器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
package Reflection;
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 获取系统类的加载器
ClassLoader systemClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(systemClassLoader);
// 获取系统类加载器的父类加载器,即扩展类加载器
ClassLoader parent = systemClassLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);
// 扩展类的父类加载器,即根加载器
ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent();
System.out.println(parent1);
// 测试当前类是哪个加载器加载的
ClassLoader classLoader = Class.forName("Reflection.Test6").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);
// 测试jdk内置的类是谁加载的
classLoader = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);
// 获取系统类加载器可以加载的路径
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.class.path"));
/**
* jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@7ad041f3
* jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$PlatformClassLoader@36baf30c
* null //根加载器获取不了
* jdk.internal.loader.ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@7ad041f3
* null
*/
}
}
例子
反射操作范型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
package Reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Test10 {
public void test1(Map<String, User> map, List<User> list){
System.out.println("test1");
}
public Map<String, User> test2(){
System.out.println("test2");
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Method method = Test10.class.getMethod("test1", Map.class, List.class);
Type[] genericParameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
for(Type type:genericParameterTypes){
System.out.println(type);
if(type instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType)type).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
method = Test10.class.getMethod("test2", null);
Type genericReturnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if(genericReturnType instanceof ParameterizedType){
Type[] actualTypeArguments = ((ParameterizedType)genericReturnType).getActualTypeArguments();
for (Type actualTypeArgument : actualTypeArguments) {
System.out.println(actualTypeArgument);
}
}
}
}
对象关系映射ORM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
package Reflection;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
public class Test11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("Reflection.Student2");
// 通过反射获得注解
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
// 获得注解的value的值
Table annotation = (Table) c1.getAnnotation(Table.class);
String value = annotation.value();
System.out.println(value);
// 获得类指定的注解
java.lang.reflect.Field f = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
Field annotation1 = f.getAnnotation(Field.class);
System.out.println(annotation1.columnName());
System.out.println(annotation1.type());
System.out.println(annotation1.length());
}
}
@Table("db_student")
class Student2{
@Field(columnName = "db_id", type = "int", length = 10)
private int id;
@Field(columnName = "db_age", type = "int", length = 10)
private int age;
@Field(columnName = "db_name", type = "varchar", length = 3)
private String name;
public Student2(){
}
public Student2(int id, int age, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student2{" +
"id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
// 类名的注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table{
String value();
}
// 属性的注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Field{
String columnName();
String type();
int length();
}
小例子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
class Tester {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
Student student = new Student(1L, "haha", "123456789012");
System.out.println(validate(student));
}
public static String validate(Object o) throws IllegalAccessException {
// 获取所有字段
Field[] fields = o.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
// 逐个检查康康那个字段上有注解
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Length.class)) {
// 获取注解详细信息
Length length = field.getAnnotation(Length.class);
field.setAccessible(true);
// 获取字段的值
int value = ((String) field.get(o)).length();
// 将字段的实际值和注解上做标示的值进行比对
if (value < length.max() || value > length.max()) {
return length.errMsg();
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Length {
int min();
int max();
String errMsg();
}
class Student {
private Long id;
private String name;
@Length(min = 11, max = 11, errMsg = "手机号码必须11位")
private String mobile;
public Student(Long id, String name, String mobile) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public Student() {
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权